Yo, listen up! Budgeting for small businesses is no joke. It’s like the secret sauce that keeps these businesses thriving and surviving in the jungle of the market. So buckle up and let’s dive into the world of budgeting for small businesses.
Creating a budget, monitoring expenses, and managing cash flow are the key players in this game. Let’s break it down and show you how to play it right.
Importance of Budgeting
Budgeting is a crucial aspect for small businesses as it helps in planning and managing finances effectively. Without a budget in place, businesses may struggle to allocate resources efficiently, leading to financial instability and potential failure.
Effective Budgeting Benefits
- Ensures Financial Stability: By setting clear financial goals and tracking expenses, businesses can maintain stability and avoid cash flow problems.
- Facilitates Decision Making: Having a budget allows businesses to make informed decisions on investments, expansions, and cost-cutting measures.
- Encourages Goal Setting: Budgeting helps businesses set achievable goals and work towards them, providing a roadmap for success.
- Identifies Areas for Improvement: Through budget analysis, businesses can identify areas where costs can be reduced or revenue increased, leading to improved efficiency.
Consequences of Not Having a Budget
- Financial Uncertainty: Without a budget, businesses may face unpredictable financial challenges, leading to potential bankruptcy or closure.
- Lack of Planning: The absence of a budget makes it difficult to plan for the future, resulting in missed opportunities and poor financial management.
- Inefficient Resource Allocation: Without a budget, businesses may overspend in certain areas while neglecting essential expenses, impacting overall profitability.
Creating a Budget
Creating a budget for a small business is crucial for financial planning and success. It involves several key steps to ensure that the business operates within its means and reaches its financial goals.
Steps in Creating a Budget
- 1. Assess Income and Expenses: Start by determining all sources of income and categorizing expenses to get a clear picture of the financial situation.
- 2. Set Financial Goals: Establish realistic and achievable financial goals that align with the business objectives.
- 3. Allocate Funds: Distribute the available funds to different expense categories based on priority and necessity.
- 4. Monitor and Adjust: Regularly track the actual income and expenses against the budgeted amounts, making adjustments as needed.
Comparison of Budgeting Methods
- 1. Zero-Based Budgeting: Every expense must be justified, starting from zero. Suitable for small businesses with fluctuating income.
- 2. Incremental Budgeting: Based on the previous period’s budget, with adjustments made for changes. Simple and easy to implement.
- 3. Activity-Based Budgeting: Focuses on activities that drive costs, providing a detailed view of expenses. Ideal for businesses with diverse operations.
Setting Realistic Financial Goals
- 1. Be Specific: Define clear and specific financial targets that are measurable and achievable.
- 2. Prioritize Goals: Identify the most critical financial goals that align with the business’s long-term vision.
- 3. Break Down Goals: Divide larger goals into smaller milestones to track progress effectively.
- 4. Review Regularly: Continuously assess the progress towards financial goals and make adjustments as necessary.
Monitoring Expenses
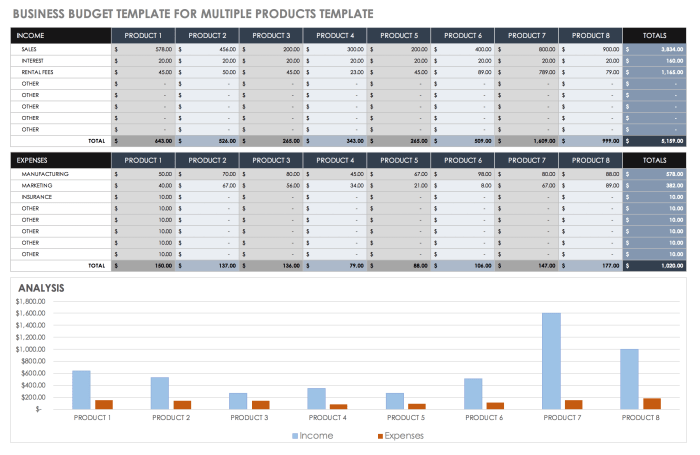
In order to effectively manage your small business budget, it is crucial to regularly monitor your expenses. By keeping a close eye on where your money is going, you can make informed decisions and ensure that you are staying on track financially.
Expense Tracking Tools and Software
- QuickBooks: A popular accounting software that allows you to track expenses, create invoices, and manage your finances all in one place.
- Expensify: An expense management tool that simplifies the process of tracking and categorizing expenses, making it easier to analyze your spending habits.
- Mint: A budgeting app that syncs with your bank accounts to track expenses, set budgets, and receive alerts for unusual spending patterns.
Identifying and Reducing Unnecessary Expenses
- Review your expenses regularly: Take the time to go through your expenses line by line to identify any areas where you may be overspending.
- Set budget limits: Establish clear budget limits for different expense categories to help control spending and avoid unnecessary costs.
- Negotiate with vendors: Reach out to your vendors to see if there are any opportunities to reduce costs or negotiate better deals on products or services.
Managing Cash Flow
Managing cash flow is crucial for the success of small businesses. It involves monitoring the flow of money in and out of the business to ensure there is enough cash on hand to cover expenses and investments.
Significance of Managing Cash Flow
Effective cash flow management helps businesses avoid financial difficulties, such as running out of cash to pay bills or make payroll. It also allows business owners to make informed decisions about spending and investments, ultimately contributing to the overall financial health of the business.
Examples of Poor Cash Flow Management
– Inadequate cash reserves can lead to missed opportunities for growth or expansion.
– Delayed payments from customers can cause cash flow shortages and hinder day-to-day operations.
– Overspending on unnecessary expenses can strain cash flow and limit the ability to invest in essential areas of the business.
Tips for Optimizing Cash Flow
- Monitor cash flow regularly to identify trends and anticipate potential shortfalls.
- Implement efficient invoicing and payment collection processes to ensure timely receipt of funds.
- Negotiate favorable payment terms with suppliers to manage cash outflows effectively.
- Reduce unnecessary expenses and prioritize spending on initiatives that generate revenue or improve efficiency.
- Consider securing a line of credit or small business loan to bridge cash flow gaps during slower periods.
